5 Array Methods in JavaScript | Part 3 | Mastering JavaScript
Hello and welcome back to our series on JavaScript array methods! If you haven't seen other parts, be sure to check out parts 1 and 2 by clicking the links in the description. In today's video, we'll be diving into five more exciting array methods.
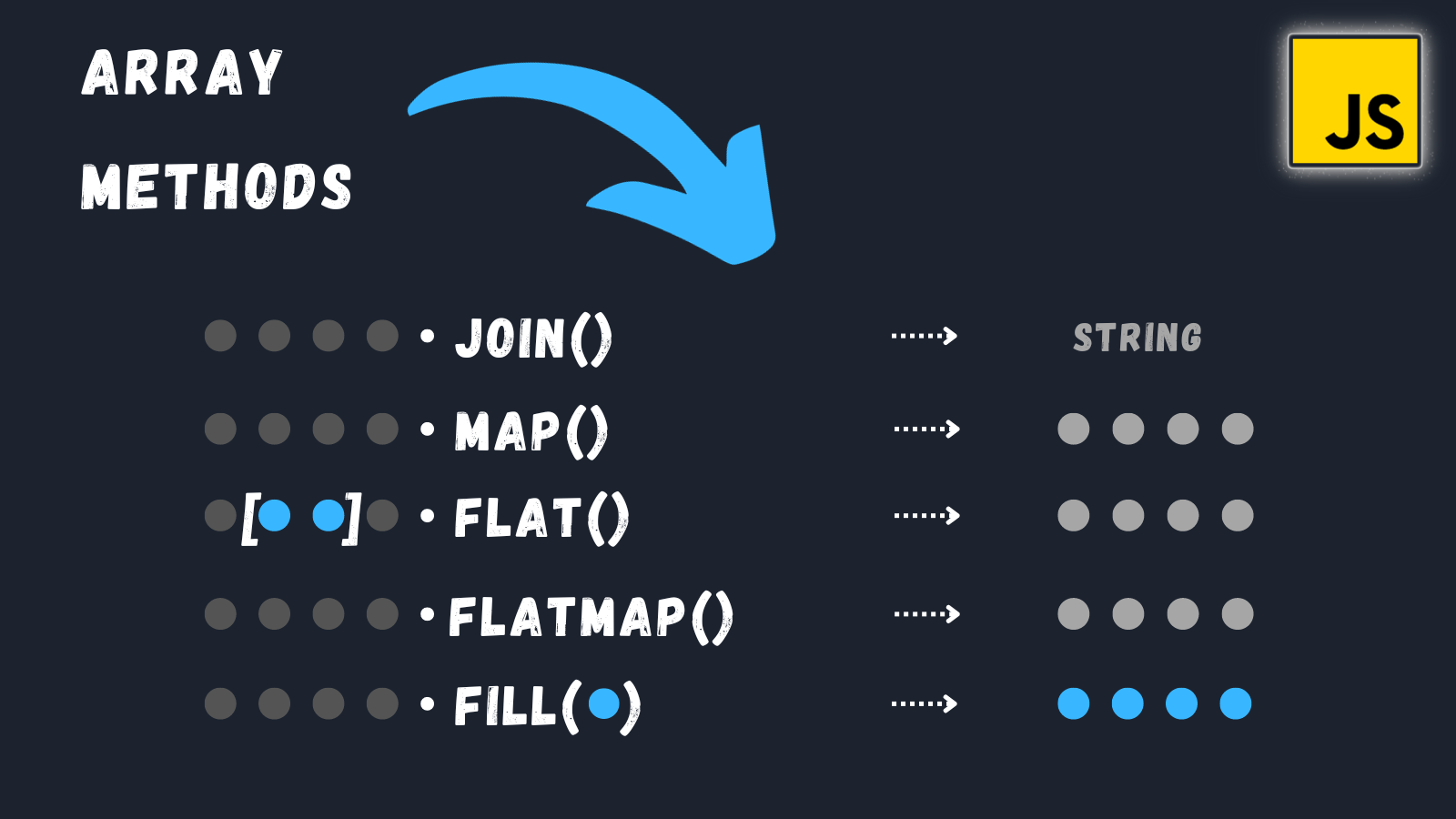
join
the join() method is used to join all the elements of an array into a single string and return that string. You can specify a delimiter, which is a string that separates each element in the resulting string. If you don't provide a delimiter, the default is a comma (,).
easy example
1const fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"];
2const result = fruits.join(', '); // Join the elements with a comma and space
3console.log(result); // Output: "apple, banana, cherry"Advanced Example:
1const books = [
2 { title: "The Catcher in the Rye", author: "J.D. Salinger", year: 1951 },
3 { title: "To Kill a Mockingbird", author: "Harper Lee", year: 1960 },
4 { title: "1984", author: "George Orwell", year: 1949 },
5 { title: "The Great Gatsby", author: "F. Scott Fitzgerald", year: 1925 }
6];
7
8let olderBookDescriptions = [];
9
10for (let i = 0; i < books.length; i++) {
11 const book = books[i];
12 if (book.year < 1960) {
13 olderBookDescriptions.push(`${book.title} by ${book.author} (${book.year})`);
14 }
15}
16
17const result = olderBookDescriptions.join('\\n');
18
19console.log(result);map
The map() method, that allows you to create a new array by applying a function to each element of an existing array. It does not modify the original array but returns a new one with the modified elements.
Easy Example:
1// Easy example: Doubling each element in an array
2const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
3
4const doubledNumbers = numbers.map(function (number) {
5 return number * 2;
6});
7
8console.log(doubledNumbers); // Output: [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]Advanced Example:
1// Advanced example: Extracting specific properties from an array of objects
2const students = [
3 { name: 'Alice', age: 22 },
4 { name: 'Bob', age: 25 },
5 { name: 'Charlie', age: 21 },
6];
7
8const studentNames = students.map(function (student) {
9 return student.name;
10});
11
12console.log(studentNames); // Output: ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie']flat
The flat() method is another built-in JavaScript array method that allows to flatten a nested array, meaning it converts a multi-dimensional array into a one-dimensional array. This method doesn't modify the original array but returns a new flattened array.
Easy Example:
1// Easy example: Flattening a nested array
2const nestedArray = [1, 2, [3, 4], [5, [6, 7]]];
3
4// flat array with one level
5const flattenedArray = nestedArray.flat();
6
7console.log(flattenedArray); // Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, [6, 7]]Advanced Example:
1// Advanced example: Flattening a deeply nested array
2const deeplyNestedArray = [1, [2, [3, [4, [5]]]]];
3
4const deeplyFlattenedArray = deeplyNestedArray.flat(Infinity);
5
6console.log(deeplyFlattenedArray); // Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
7
8flatmap
The flatMap() method is a combination of the map() and flat() methods. it use to apply a function to each element of an array and then flatten the result into a new array. Like map() method, it does not modify the original array but returns a new one.
Easy Example:
1// Easy example: Using flatMap to double and flatten elements in an array
2const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
3
4const doubledAndFlattened = numbers.flatMap(function (number) {
5 return [number * 2];
6});
7
8console.log(doubledAndFlattened); // Output: [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]Advanced Example:
1// Advanced example: Flattening and extracting data from an array of objects
2const people = [
3 { name: 'Alice', hobbies: ['reading', 'painting'] },
4 { name: 'Bob', hobbies: ['coding', 'gaming'] },
5 { name: 'Charlie', hobbies: ['swimming', 'cooking'] },
6];
7
8const allHobbies = people.flatMap(function (person) {
9 return person.hobbies;
10});
11
12console.log(allHobbies); // Output: ['reading', 'painting', 'coding', 'gaming', 'swimming', 'cooking']fill
final method in this video is The fill() method which is used to fill all or a portion of an array with a static value. It modifies the original array and returns the modified array.
Easy Example:
1// Easy example: Filling an array with a static value
2const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
3
4// Fill the entire array with the value 0
5array.fill(0);
6
7console.log(array); // Output: [0, 0, 0, 0, 0]Advanced Example:
1// Advanced example: Filling a portion of an array with a specific value
2const colors = ['red', 'green', 'blue', 'yellow', 'orange'];
3
4// Fill a portion of the array starting from index 1 to index 3 with the value 'purple'
5colors.fill('purple', 1, 4);
6
7console.log(colors); // Output: ['red', 'purple', 'purple', 'purple', 'orange']Do not forget to like, share, and subscribe to the channel. see you in next one.