5 Array Methods in JavaScript | Part 1 | Mastering JavaScript
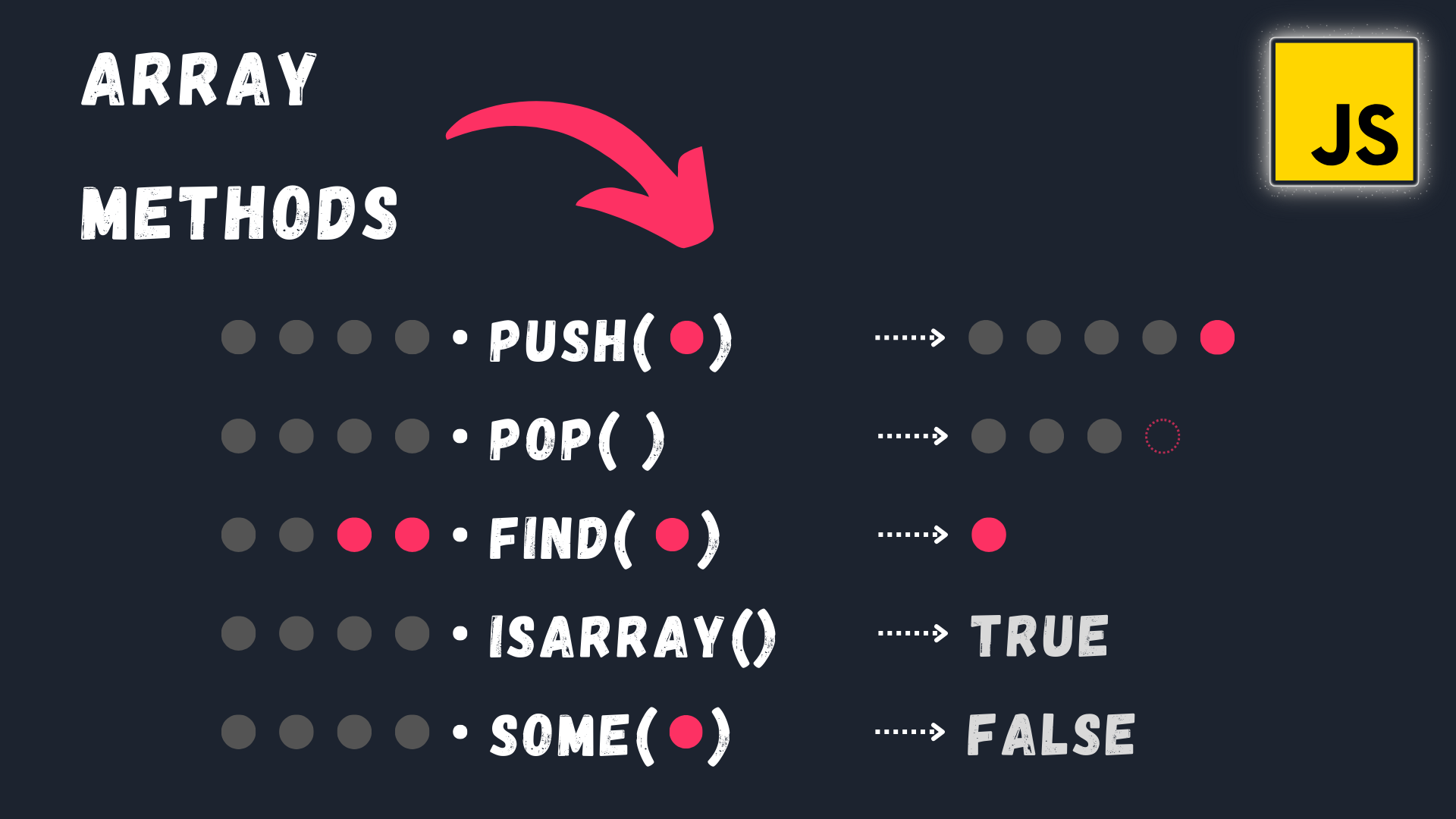
Hey and welcome to another video in Mastering JavaScript series in this video we gonna take look at 5 array methods and they are push, pop, find, isArray and some. understanding each one use cases, without further to say.
let's get start with first method which is push.
PUSH
The push() method is used to add one or more elements to the end of an array and returns the new length of the array. It mutates the original array by adding the specified element(s) to it. This method is commonly used to dynamically grow an array by appending new values to it.
Easy Example:
1// Define an empty array
2let fruits = [];
3
4// Use push() to add elements to the array
5fruits.push("apple");
6fruits.push("banana");
7fruits.push("cherry");
8
9console.log(fruits); // Output: ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]Advanced Example:
1// Define an array of numbers
2let numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
3
4// Define a function to generate and push squares of numbers
5function pushSquares(arr, n) {
6 for (let i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
7 arr.push(i * i);
8 }
9}
10
11// Use the pushSquares function to add squares of numbers up to 7
12pushSquares(numbers, 7);
13
14console.log(numbers); // Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49]POP
the second method in list is the pop() method is used to remove and return the last element from an array. It mutates the original array by removing the last element.
Easy Example:
1// Define an array of colors
2let colors = ["red", "green", "blue", "yellow"];
3
4// Use pop() to remove and return the last color
5let lastColor = colors.pop();
6
7console.log(lastColor); // Output: "yellow"
8console.log(colors); // Output: ["red", "green", "blue"]Advanced Example:
1// Define an array of tasks
2let tasks = [
3 { id: 1, description: "Write code", completed: false },
4 { id: 2, description: "Read documentation", completed: false },
5 { id: 3, description: "Test functionality", completed: true }
6];
7
8// Define a function to remove and return the last task
9function popLastTask(arr) {
10 if (arr.length === 0) {
11 return null; // Return null if the array is empty
12 } else {
13 return arr.pop();
14 }
15}
16
17// Use the popLastTask function to remove the last task
18let removedTask = popLastTask(tasks);
19
20console.log(removedTask); // Output: { id: 3, description: "Test functionality", completed: true }
21console.log(tasks); // Output: [{ id: 1, description: "Write code", completed: false }, { id: 2, description: "Read documentation", completed: false }]FIND
next method, the find() method is used to search for the first element in an array that satisfies a given condition and returns that element. If no element satisfies the condition, it returns undefined.
Easy Example:
1// Define an array of numbers
2let numbers = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9];
3
4// Use find() to find the first even number
5let evenNumber = numbers.find(function (element) {
6 return element % 2 === 0;
7});
8
9console.log(evenNumber); // Output: undefined (no even number found)Advanced Example:
1// Define an array of objects representing books
2let books = [
3 { id: 1, title: "The Catcher in the Rye", author: "J.D. Salinger" },
4 { id: 2, title: "To Kill a Mockingbird", author: "Harper Lee" },
5 { id: 3, title: "1984", author: "George Orwell" },
6 { id: 4, title: "The Great Gatsby", author: "F. Scott Fitzgerald" }
7];
8
9// Define a function to find a book by its title
10function findBookByTitle(title) {
11 return books.find(function (book) {
12 return book.title === title;
13 });
14}
15
16// Use the findBookByTitle function to find a book by title
17let book = findBookByTitle("1984");
18
19console.log(book); // Output: { id: 3, title: "1984", author: "George Orwell" }IsArray
fourth method, the Array.isArray() method is used to check if a given value is an array or not. It returns true if the value is an array and false otherwise.
Easy Example:
1// Check if a variable is an array
2let fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"];
3let number = 42;
4
5console.log(Array.isArray(fruits)); // Output: true
6console.log(Array.isArray(number)); // Output: falseAdvanced Example:
1// Define a function that accepts an array and checks its type
2function processArray(arr) {
3 if (Array.isArray(arr)) {
4 console.log("Processing the array:", arr);
5 // Perform array-specific operations here
6 } else {
7 console.log("Input is not an array:", arr);
8 // Handle non-array input
9 }
10}
11
12let myArray = [1, 2, 3];
13let myString = "Hello, World!";
14
15processArray(myArray); // Output: Processing the array: [1, 2, 3]
16processArray(myString); // Output: Input is not an array: Hello, World!SOME
final method, the some() method is used to check if at least one element in an array satisfies a given condition. It returns true if at least one element meets the condition, otherwise, it returns false.
Easy Example:
1// Check if there is at least one even number in an array
2let numbers = [1, 3, 5, 6, 7, 9];
3
4let hasEvenNumber = numbers.some(function (element) {
5 return element % 2 === 0;
6});
7
8console.log(hasEvenNumber); // Output: true (6 is an even number)Advanced Example:
1// Define an array of objects representing users
2let users = [
3 { id: 1, name: "Alice", isAdmin: true },
4 { id: 2, name: "Bob", isAdmin: false },
5 { id: 3, name: "Charlie", isAdmin: false },
6 { id: 4, name: "David", isAdmin: true }
7];
8
9// Check if there is at least one admin user
10let hasAdminUser = users.some(function (user) {
11 return user.isAdmin === true;
12});
13
14console.log(hasAdminUser); // Output: true (Alice and David are admin users)conclusion
As we wrap up, I'd like to express my gratitude for your engagement up to this point. If you have any questions, please don't hesitate to ask in the video comments section. Also, if you find value in content, dot not forget to like video and subscribing to channel. Stay tuned for more exciting content in the future!